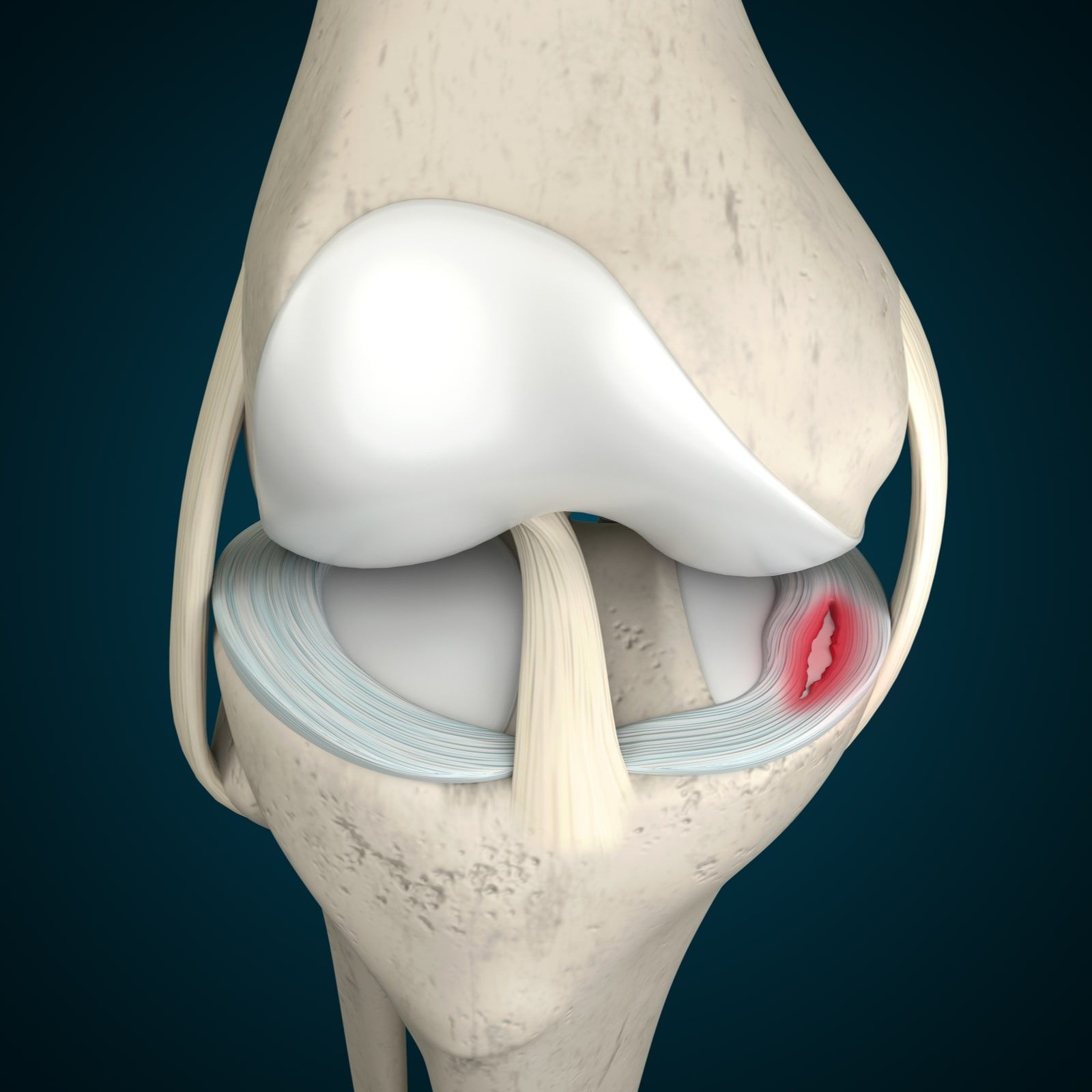
Cartilage is a tough, flexible connective tissue found throughout the body, serving as a cushion between bones and helping to facilitate smooth joint movement. It provides structure and support to various parts of the body, including the joints, ears, nose, and trachea.
Did you know?
Cartilage lacks blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels, making it a challenging tissue to heal. However, recent advancements in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering hold promise for developing innovative treatments to repair and regenerate damaged cartilage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of cartilage injuries?
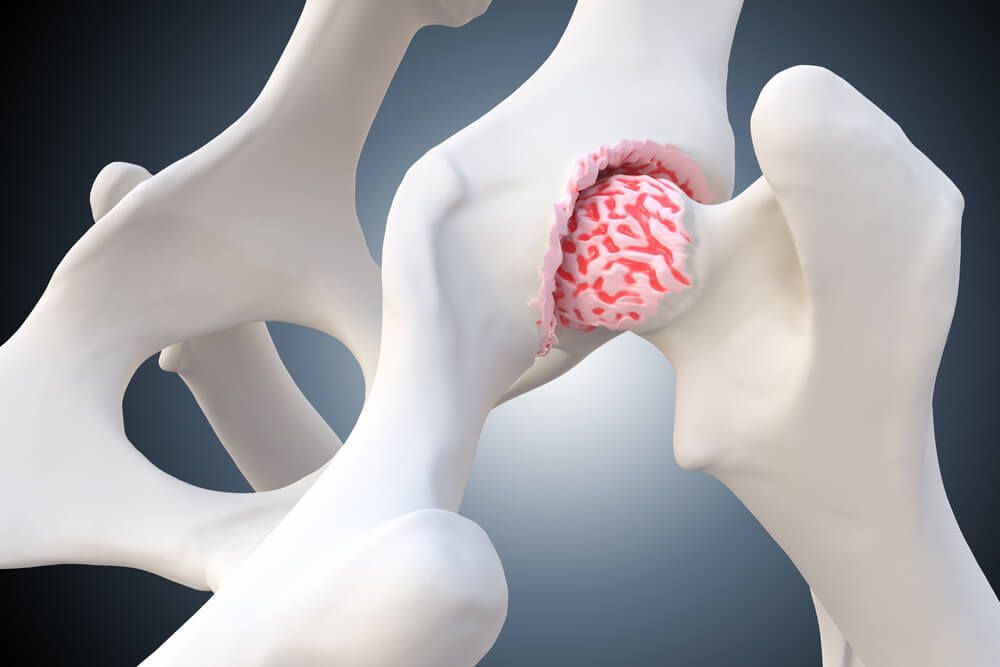
- Articular Cartilage Injury: This type of injury affects the smooth, white cartilage covering the ends of bones in joints, such as the knee, hip, and shoulder. Articular cartilage injuries can occur due to trauma, repetitive stress, or degenerative conditions like osteoarthritis.
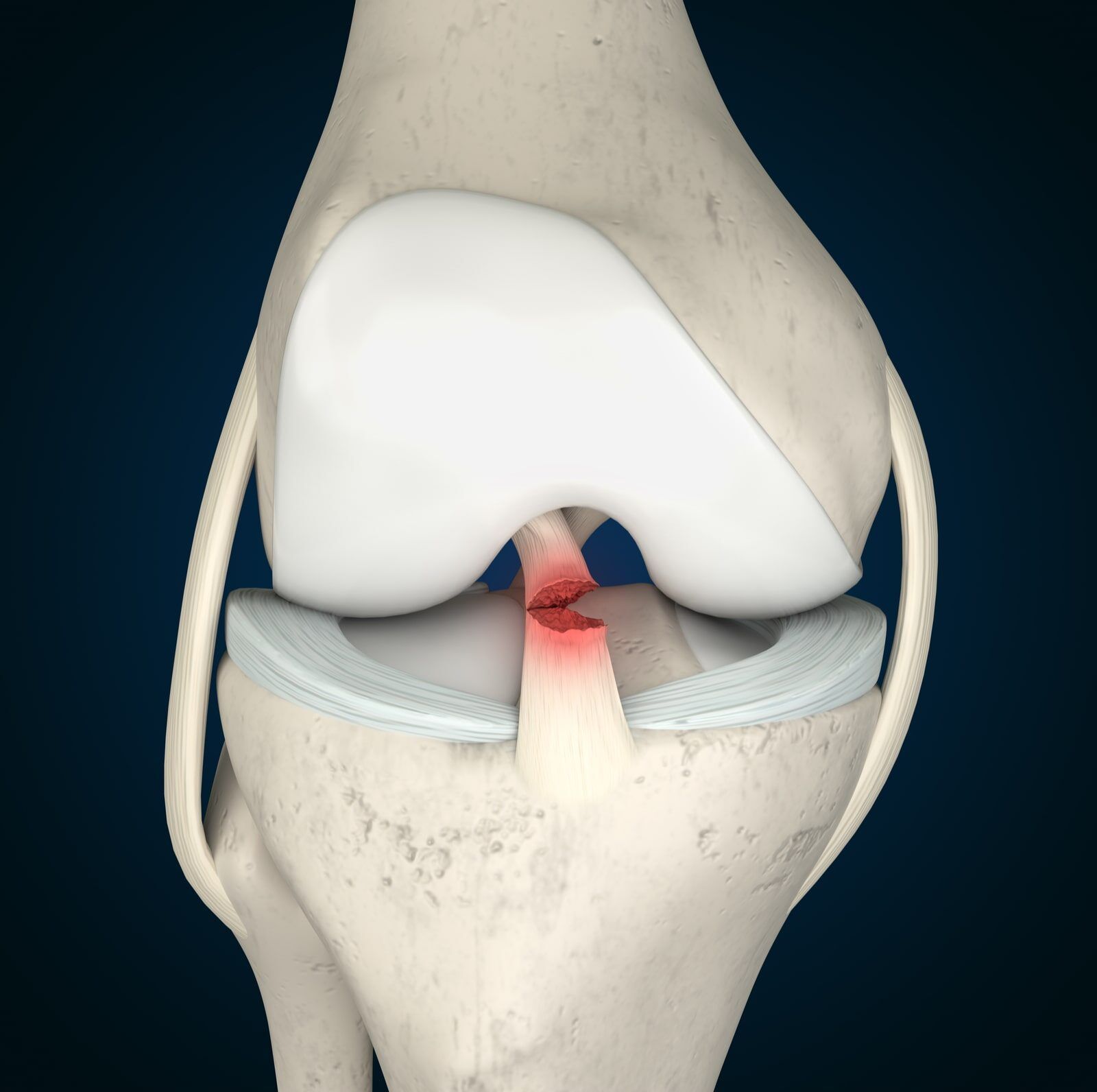
- Meniscus Tear: The meniscus is a rubbery cartilage pad located in the knee joint, acting as a shock absorber and stabilizer. Tears in the meniscus can result from sudden twisting or forceful impact to the knee, leading to pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
- Hyaline Cartilage Injury: Hyaline cartilage is a type of cartilage found in the ribs, larynx, and trachea, as well as covering the ends of bones in joints. Injuries to hyaline cartilage can occur due to trauma, wear and tear, or underlying medical conditions, causing pain and dysfunction in affected areas.
What causes cartilage injuries?
Cartilage injuries can result from trauma, repetitive stress, degenerative conditions like osteoarthritis, or underlying medical conditions.
How are cartilage injuries diagnosed?
Cartilage injuries are diagnosed through physical examination, imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans, and possibly arthroscopic evaluation for a more detailed assessment of the joint.
What are the treatment options for cartilage injuries?
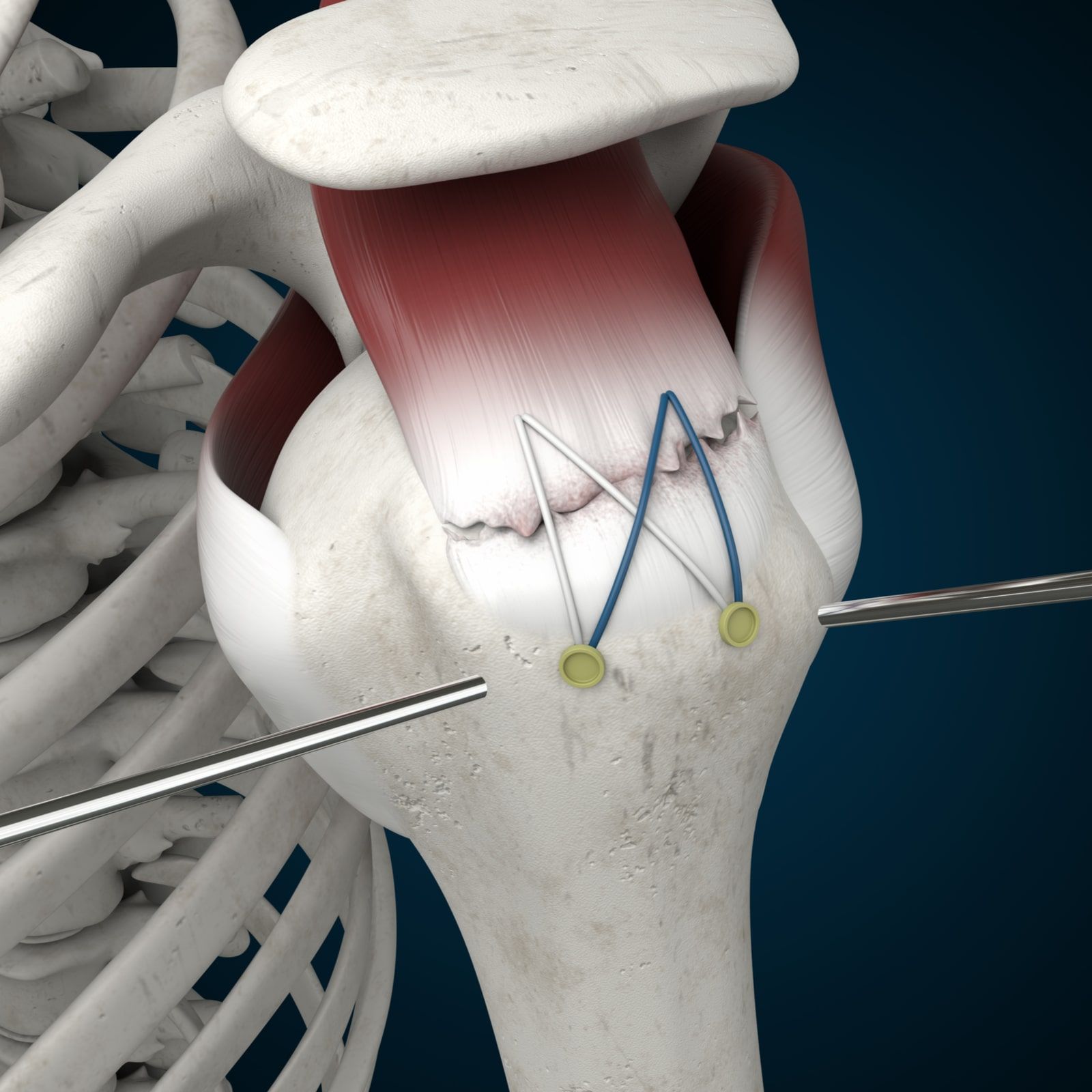
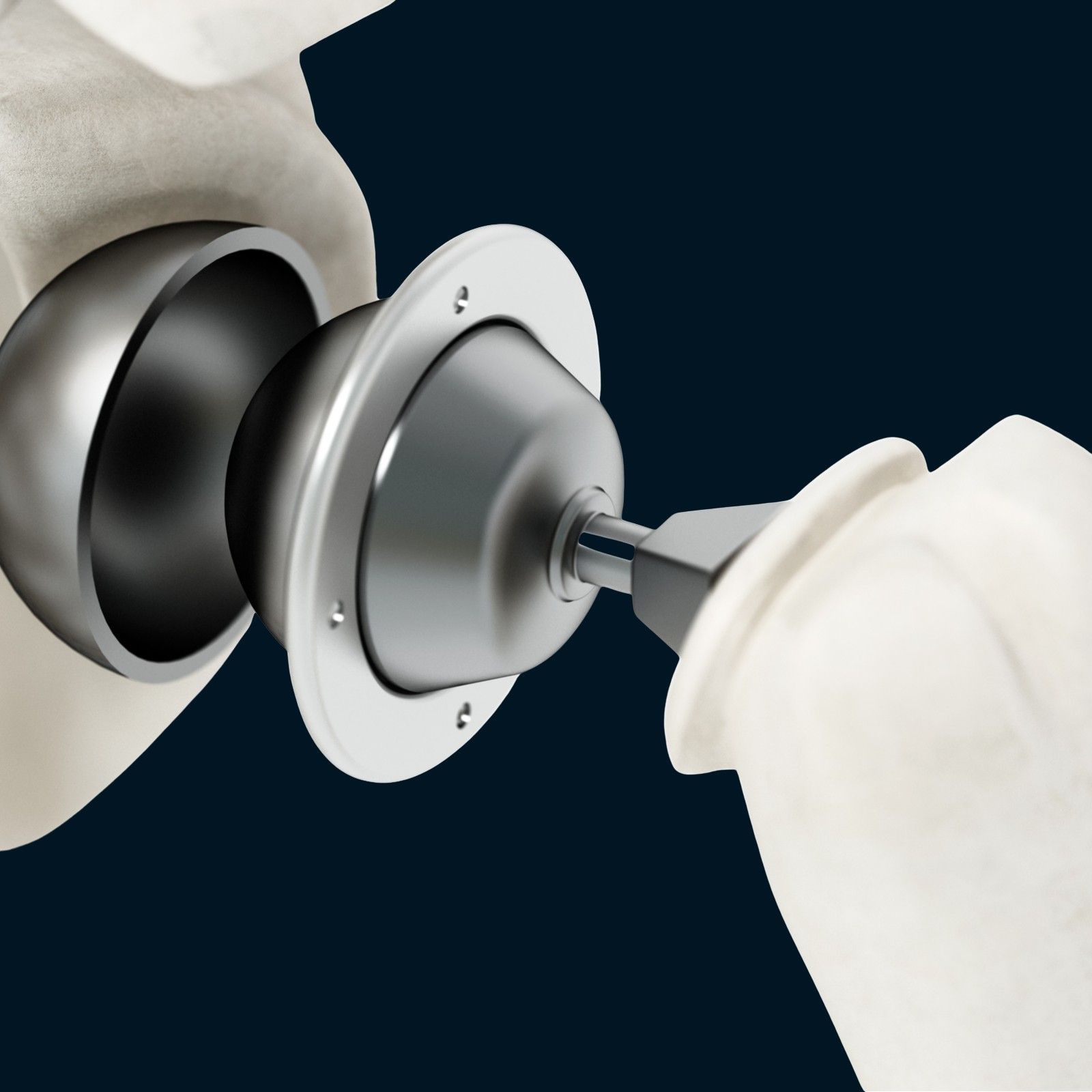
Treatment options may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) therapy, physical therapy exercises, medications, corticosteroid injections, or surgical interventions such as arthroscopic debridement or cartilage restoration procedures.